DNA extension for ABCD - Mapping ExampleThe following boxws should lead you through important
or required ABCDDNA attributes in mapping. If you have further questions
please contact
Gabi Droege (g.droege@bgbm.org). |
|
|
|
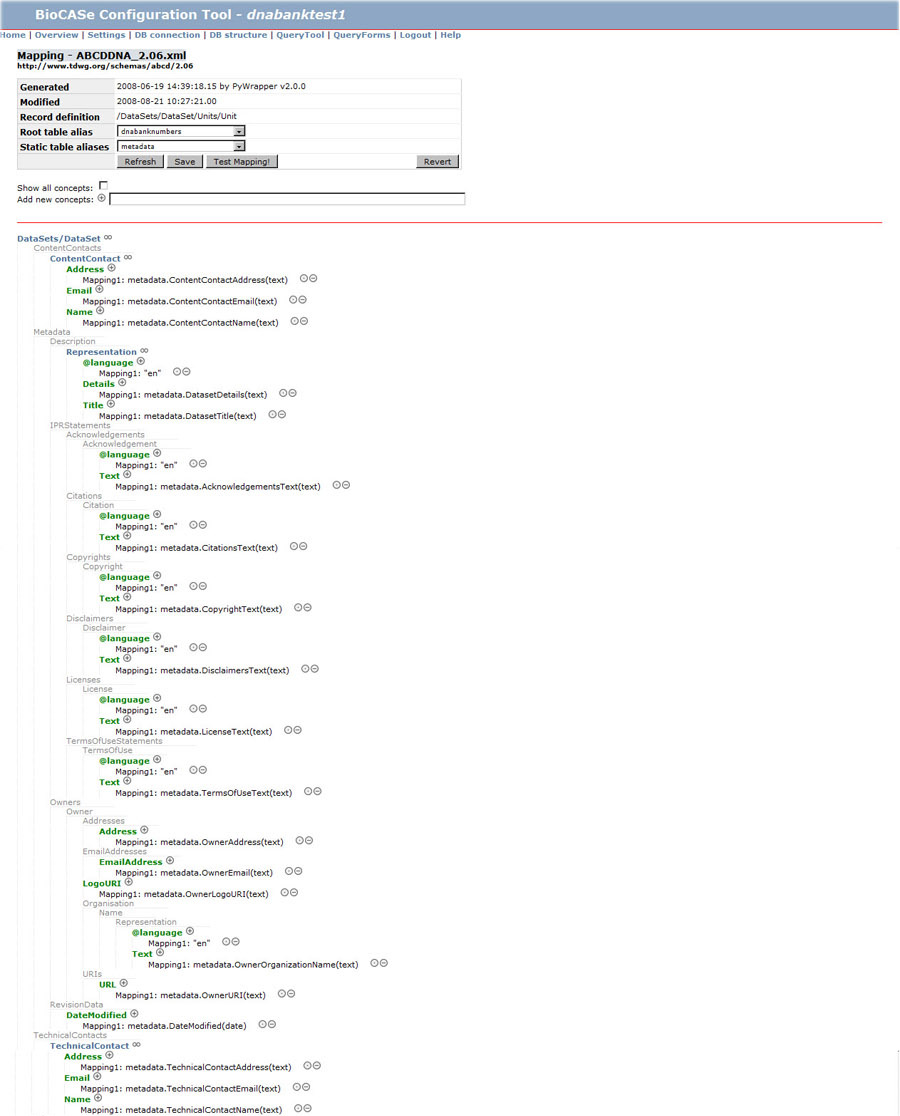
Fig. 6. Mapping with ABCDDNA - Metadata. The
root and static table alias should be defined at first. The root table
should include the UnitIDs which are unique 'DNA Bank Numbers'
in that case.
Static table alias applies for all data and is mostly defined as
the Metadata table. It is very important to define contact persons as
well as legal rights for using the DNA data. Finally, it is impossible
to see the data via wrapper if the Metadata has not been mapped. |
Related Specimen data: |
 |
|
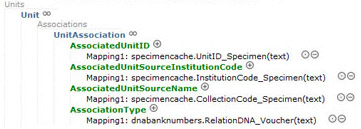
Fig. 7. Mapping with ABCDDNA - UnitAssociation. The
actual Unit data including all DNA data and some rudimental
specimen information are listed following the
Metadata. It is absolutely essential
to map both the Triple Identifier for the related voucher/specimen
(UnitAssociation) and the mandatory feature
'AssociationType'. All UnitAssociation data won't be visible
otherwise. For further information please click here. |
 |
|
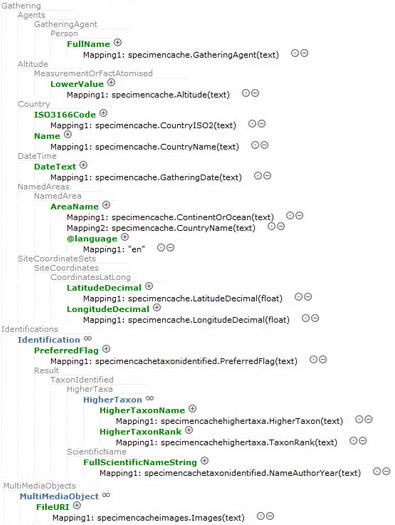
Fig. 8. Mapping with ABCDDNA - Gathering and Identification.
The 'Gathering' and 'Identification' part
has to be mapped that these data can be loaded into the web index of the DNA Bank Network's web
portal. If such data, e.g. 'Taxon Name' or 'Country', are not in
the web index searches for them won't be succesful. For that
matter it would be as well advantageous to map specimen images as 'MultiMediaObject'.
Search results in the web portal can than be limited to samples
only if a digital image to the related
voucher/specimen of a DNA sample exists.
Note: There is another
attribute for an image URL within the part 'DNA Sample'. Please
pay
attention to correctly map the image URL for the specimen images and for the DNA
such as gel images by applying the appropriate ABCD attribute! |
DNA data:Some attributes of the basic ABCD 2.06 schema such as 'KindOfUnit', 'RecordBasis', 'UnitID', 'SourceID', 'SourceInstitutionID' and the Metadata (see Fig. 6) have to be mapped in the DNA context. |
 |
|
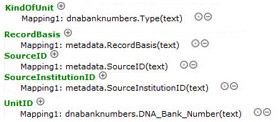
Fig. 9. Mapping with ABCDDNA - Kind of Unit, Record Basis,
SourceID, SourceInstitutionID, UnitID. 'Kind of Unit'
indicates the type of DNA isolated, e.g. mitochondrial or
genomic DNA.
'RecordBasis' has to be mapped as 'OtherSpecimen', because no
other option for 'DNA sample' is provided in the ABCD
2.06 vocabulary (details). Since ABCD Unit is synonymous to DNA sample as a certain sample type the UnitID has to be mapped as the (unique) 'DNA Bank Number'. Furthermore 'SourceID' could, for example, be mapped as 'DNA Bank' and 'SourceInstitutionID' as the institution holding the collection. |
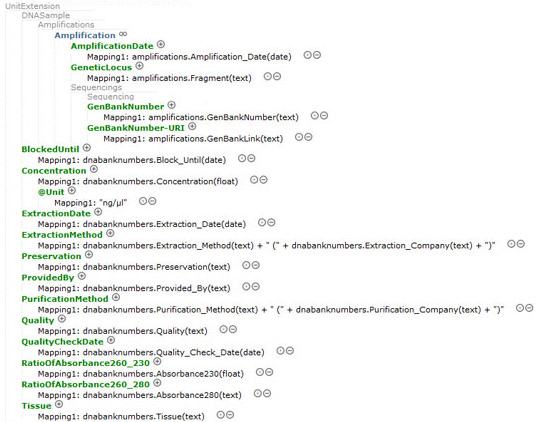 |
| Fig. 10. Mapping with ABCDDNA - Detail of the DNA extension. The lately created DNA part of the mapping schema covers more than 35 elements such as 'ExtractionDate', 'ExtractionMethod' for DNA extraction as well as an 'Amplification Container' for sequences, GenBank Numbers, clone strains etc. Note that 'Amplification Container' subsumes data of more than one amplification if necessary. Most of the other ABCDDNA attributes (DNA part) have a one-to-one relation to the UnitID that is every Unit (every UnitID) has, for example, only one 'ExtractionDate'. |